Introduction to Drone Swarm Technology and Security Risks
Drone swarm technology represents a fundamental shift in how unmanned aerial systems are deployed and managed. Understanding its operational logic and associated security risks is essential for evaluating why traditional low-altitude defense measures are increasingly inadequate when faced with coordinated swarm-based threats.
What Is a Drone Swarm?
Drone swarm technology is a distributed application of unmanned aerial vehicles (БПЛА) that mimics the collective behavior of natural swarms such as bees or birds. Through inter-drone communication and collaborative algorithms, multiple drones can share information, coordinate tasks, and execute missions as an integrated system rather than as isolated platforms.
How Drone Swarms Differ from Single UAV Operations?
Unlike traditional single-drone operations, drone swarms emphasize decentralization, redundancy, and cooperation. Each drone functions as a node within a network, enabling real-time data exchange, adaptive path planning, and coordinated decision-making. This significantly enhances operational flexibility, mission efficiency, and resilience against partial system failures.
Why Drone Swarms Pose a New Low-Altitude Security Challenge?
While drone swarms bring efficiency and scalability to civilian and military applications, their rapid development has introduced serious security risks. Incidents involving drone swarms disrupting airport operations, conducting unauthorized surveillance, and stealing sensitive information have already occurred worldwide. Compared to single UAV threats, swarm attacks characterized by large numbers, high speed, and strong coordination present unprecedented challenges to traditional low-altitude security and air defense systems.

Drone Swarm
Key Threat Characteristics of Drone Swarm Attacks
Drone swarm attacks differ significantly from conventional UAV threats due to their scale, coordination, and adaptability. By analyzing the core threat characteristics of drone swarms, security planners can better assess risk levels and design countermeasures tailored to swarm-based attack scenarios.
Sudden and Stealthy Multi-Directional Attacks
Individual drones within a swarm are typically small in size and have extremely low radar cross-sections, sometimes as low as 0.01 square meters. Flying at low or very low altitudes, they can exploit terrain masking to covertly approach targets. Drone swarms can launch simultaneous attacks from multiple directions, making attack timing and vectors highly unpredictable and leaving defenders with minimal early-warning windows.
Coordinated Mass Attacks and Destructive Potential
Although the payload capacity of a single drone is limited, a swarm’s numerical advantage and coordinated attack capability can result in significant damage. Drone swarms can carry explosives, incendiary devices, or other payloads to strike critical infrastructure such as power substations, communication base stations, and transportation hubs. Precision strikes on key components like transformers or circuit breakers can cause widespread service disruptions and cascading societal impacts.
Information Jamming, Reconnaissance, and Data Theft
Drone swarms also possess strong information warfare capabilities. By deploying electronic jamming equipment, they can interfere with communication networks, radar systems, and navigation infrastructure, potentially rendering them inoperable. In parallel, onboard sensors such as cameras and signal receivers enable large-scale data collection. In military contexts, this supports battlefield intelligence gathering; in civilian environments, it raises severe concerns regarding industrial espionage and personal data security.
Why Drone Swarms Are Difficult to Detect, Track, and Intercept?
The large number of targets and the high degree of coordination within drone swarms overwhelm traditional defense systems. High-cost air defense missiles are economically unsustainable against low-cost drones, while their reaction speed and interception capacity are often insufficient. Moreover, drone swarms can dynamically reconfigure their formations and tactics in response to countermeasures, further complicating continuous tracking and sustained interception.
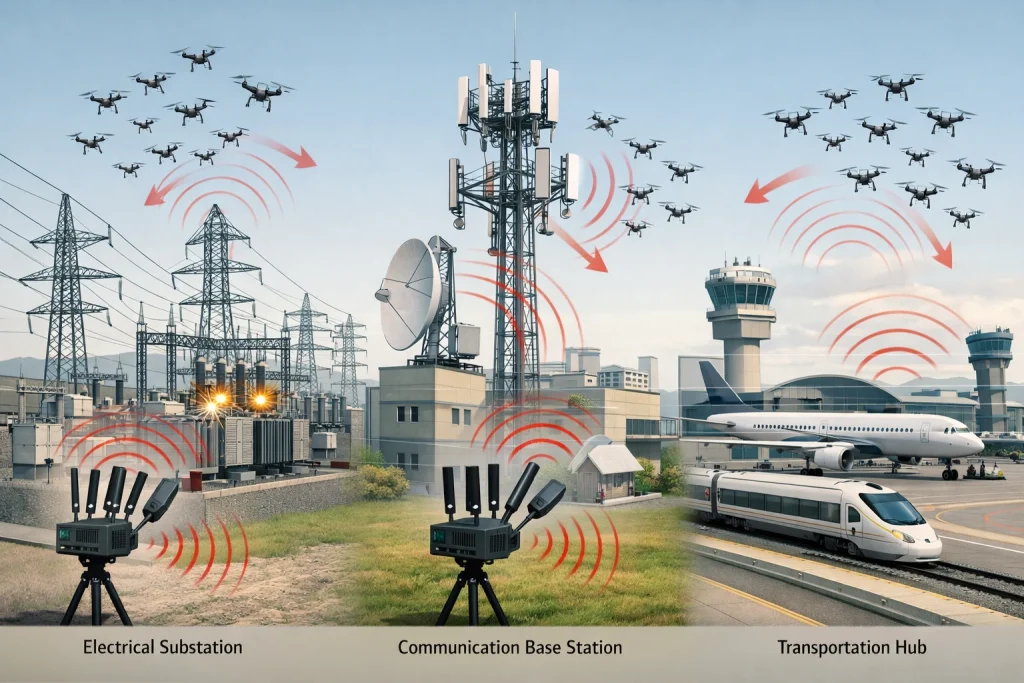

Why Traditional Counter-Drone Systems Struggle Against Swarms
Most existing counter-drone systems were originally designed to address isolated or low-density UAV intrusions. When confronted with large-scale, coordinated drone swarms, these systems reveal structural and economic limitations that significantly reduce their defensive effectiveness.
Limitations of Single-Target Detection Systems
Conventional counter-drone systems are primarily designed to detect and engage individual UAVs. In swarm scenarios, these systems struggle to maintain stable tracking across multiple low-altitude, slow-moving, and closely spaced targets, resulting in detection gaps and delayed responses.
Cost Imbalance Between Drones and Conventional Air Defense
The economic asymmetry between drone swarms and traditional air defense solutions is stark. A single interceptor missile can cost hundreds of thousands of dollars, while individual drones in a swarm may cost only a few hundred dollars. This imbalance makes conventional kinetic interception strategies impractical for large-scale swarm threats.
Reaction Speed and Saturation Problems
Drone swarms can saturate detection and interception systems through sheer numbers. Even when some drones are neutralized, others can adapt their routes and continue the mission, reducing overall interception success rates in simulated and real-world scenarios.
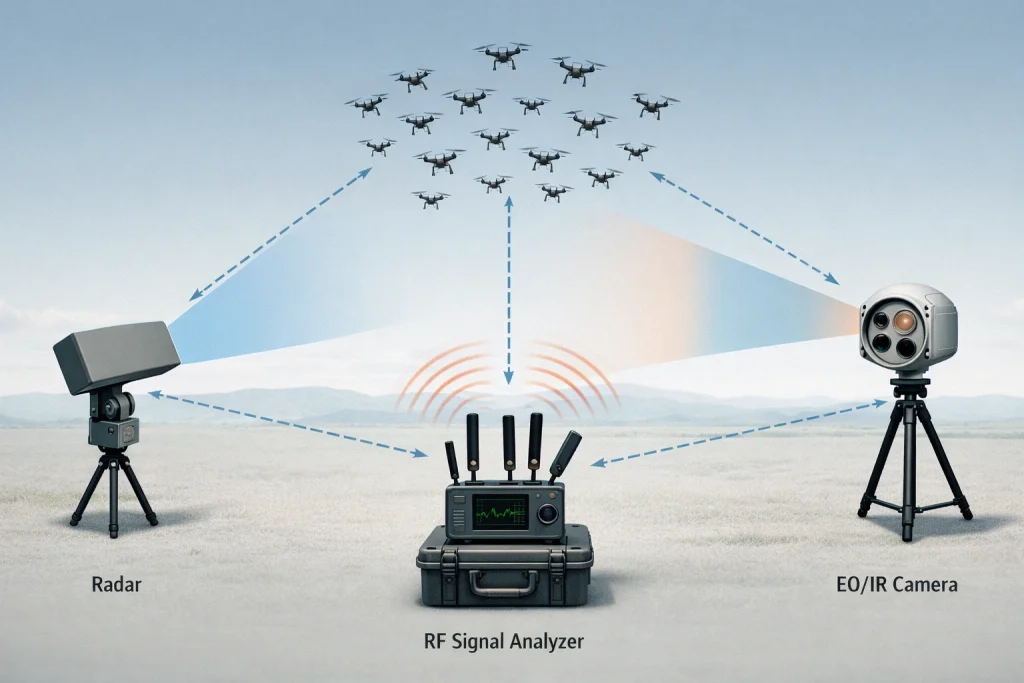
Detection Technologies for Counter-Drone Swarm Systems
Effective counter-drone swarm defense begins with reliable detection and early warning. Detecting multiple low-altitude, low-speed, and small UAVs simultaneously requires the integration of complementary sensing technologies capable of operating in complex electromagnetic and environmental conditions.
Radar Detection for Drone Swarms
Radar remains a foundational detection method in counter-drone systems. Multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) radar enhances the detection of low-altitude, low-speed, and small targets by transmitting multiple orthogonal signals. Synthetic aperture radar (SAR) further enables imaging and trajectory tracking of drone swarms over extended distances. Однако, radar performance can degrade in complex electromagnetic environments, necessitating advanced anti-interference algorithms and signal processing techniques.
Electro-Optical and Infrared Detection Technologies
Electro-optical detection combines visible-light and infrared sensing to identify drone swarms. Infrared sensors detect thermal emissions from motors and power systems, offering high sensitivity in low-altitude environments. Visible-light cameras, when integrated with artificial intelligence-based image recognition algorithms, can classify drone types and track flight paths in real time. Adverse weather conditions such as fog, дождь, or low visibility remain a key limitation, driving the need for adaptive image enhancement technologies.
Читать далее: Электрооптический & Системы акустического обнаружения для защиты от роя дронов
Acoustic Detection of Low-Altitude Drone Swarms
Acoustic detection systems use microphone arrays to capture drone noise signatures at specific frequencies. By applying signal processing algorithms, these systems can estimate drone position, speed, and quantity. Acoustic detection is particularly effective in urban or complex terrain environments, though environmental noise interference remains a significant challenge requiring ongoing improvements in noise filtering and feature extraction.
Radar RF GPS jamming comparison for counter-drone technologies
Jamming Technologies Used Against Drone Swarms
Jamming technologies form a core component of active counter-drone swarm defense by disrupting communication, навигация, and sensing capabilities. Different jamming approaches offer distinct advantages depending on engagement distance, environmental constraints, and the scale of the drone swarm threat.
Радиочастота (РФ) Технология подавления
RF jamming disrupts drone communication links and control channels by transmitting interference signals at specific frequencies. Directional RF jamming devices can precisely target individual drones at short ranges, while vehicle-mounted systems provide broader coverage capable of interfering with multiple drones simultaneously. As drone anti-jamming capabilities evolve, RF jamming strategies must continuously adapt through optimized frequency management and power allocation.
GPS Jamming and Navigation Disruption
GPS jamming interferes with satellite navigation signals by emitting high-power electromagnetic interference at the same frequencies. When drone receivers are overwhelmed by jamming signals, they may lose accurate positioning, timing, and speed data, leading to disorientation or mission failure. Handheld GPS jammers are suitable for short-range, rapid-response scenarios, while fixed systems can create large-area protective zones around airports, военные базы, and other critical facilities.
Laser Jamming and Electro-Optical Suppression
Laser jamming uses high-energy beams to blind or damage drone optical sensors, degrading their navigation and mission execution capabilities. This method offers high precision, быстрый ответ, and minimal electromagnetic impact on surrounding systems. Однако, laser effectiveness is highly dependent on weather conditions, requiring adaptive emission and tracking mechanisms to mitigate atmospheric attenuation.
Swarm Control Technologies for Coordinated Countermeasures
As drone swarms become more autonomous and coordinated, countermeasures must move beyond individual target suppression. Swarm control technologies focus on influencing or disrupting collective behavior, enabling defenders to neutralize multiple drones through systemic intervention.
What Is Swarm Control in Counter-Drone Systems?
Swarm control technology focuses on disrupting the collaborative logic and decision-making mechanisms of drone swarms rather than targeting individual platforms. By interfering with swarm communication networks and coordination algorithms, defenders can suppress, fragment, or neutralize multiple drones simultaneously.
Swarm Communication Jamming and Network Disruption
This approach targets the communication protocols that enable swarm coordination. By emitting tailored jamming signals or protocol-specific interference, swarm formations can be destabilized, reducing their operational effectiveness. Continuous adaptation is required as swarm communication protocols become more encrypted and sophisticated.
Deceptive Jamming and False Command Injection
Deceptive jamming misleads drone swarms by injecting false navigation data or control commands. This can cause drones to deviate from intended paths, misidentify targets, or return to incorrect locations. Successful implementation requires deep knowledge of swarm control algorithms and real-time monitoring to dynamically adjust deceptive signals.
Intelligent Counter-Drone Swarm Systems and AI-Based Defense
Artificial intelligence introduces a new level of adaptability and automation to counter-drone swarm operations. By leveraging data-driven analysis and predictive algorithms, intelligent defense systems can respond more effectively to dynamic and rapidly evolving swarm threats.
AI-Driven Threat Recognition and Behavior Analysis
Artificial intelligence enables real-time monitoring and analysis of drone swarm behavior. Machine learning algorithms can identify attack patterns, predict swarm intentions, and provide early warnings before coordinated actions are executed.
Predictive Defense and Automated Countermeasure Allocation
Intelligent counter-drone systems can automatically allocate detection, глушение, and interception resources based on real-time threat assessments. This improves response speed and operational efficiency in complex and rapidly evolving environments.
Challenges of Data, Algorithms, and System Security
Despite their advantages, AI-based countermeasures require large volumes of high-quality training data and robust computing resources. They also face risks related to algorithm spoofing and adversarial attacks, necessitating continuous improvements in system security and robustness.
Integrated Counter-Drone Swarm Defense Solutions and Use Cases
In real-world deployments, counter-drone swarm effectiveness depends on how well detection, глушение, and control technologies are integrated into cohesive defense solutions. Different operational environments require tailored system architectures and deployment strategies.
Protecting Airports and Critical Infrastructure
Integrated counter-drone systems combining radar, electro-optical sensors, and jamming technologies are essential for protecting airports, power facilities, and communication hubs from drone swarm intrusions and attacks.
Military Bases and Sensitive Facility Defense
In military environments, layered and intelligent counter-drone swarm defenses provide early warning, coordinated suppression, and sustained protection against large-scale swarm attacks.
Large-Scale Events and Urban Security Scenarios
For large public events and urban areas, mobile and flexible counter-drone solutions enable rapid deployment and localized protection against unauthorized drone swarms.
Future Trends in Drone Swarm Threats and Counter-Drone Technologies
The technological evolution of drone swarms and countermeasures is ongoing. Anticipating future threat patterns and defense requirements is critical for maintaining long-term security effectiveness in both civilian and military domains.
Increasing Autonomy and Intelligence of Drone Swarms
Advances in autonomous control and artificial intelligence will further enhance the adaptability and coordination of drone swarms, increasing the complexity of associated threats.
Evolution Toward Multi-Layer and System-of-Systems Defense
Future counter-drone strategies will increasingly rely on multi-layered, integrated systems that combine detection, глушение, deception, and intelligent control across different operational domains.
Regulatory and Security Implications
As drone swarm capabilities expand, regulatory frameworks and security policies must evolve to address emerging risks while supporting legitimate applications.
Conclusion – Building Effective Defense Against Drone Swarm Threats
Drone swarm threats represent a persistent and evolving challenge for low-altitude security. Drawing together the technical analysis and defense strategies discussed above provides a foundation for informed decision-making and long-term counter-drone planning.
Why Multi-Sensor and Multi-Layer Defense Is Essential
Drone swarm threats cannot be effectively mitigated through single-point solutions. Multi-sensor fusion and layered defense architectures are critical for achieving reliable detection, timely response, and sustained protection.
Key Takeaways for Security and Defense Decision-Makers
To address the growing risks posed by drone swarms, stakeholders must invest in integrated, разумный, and adaptable anti drone swarm technologies that balance effectiveness, cost efficiency, and operational flexibility.
 РагинТех
РагинТех


